Overview
A single client is considered authenticated as long as it sends valid
Authorization:YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN header with the request.
The PocketBase Web APIs are fully stateless and there are no sessions in the traditional sense (even the tokens are not stored in the database).
Because there are no sessions and we don't store the tokens on the server there is also no logout
endpoint. To "logout" a user you can simply disregard the token from your local state (aka.
pb.authStore.clear() if you use the SDKs).
The auth token could be generated either through the specific auth collection Web APIs or programmatically via Go/JS.
All allowed auth collection methods can be configured individually from the specific auth collection options.
Note that PocketBase admins (aka. _superusers) are similar to the regular auth
collection records with 2 caveats:
- OAuth2 is not supported as auth method for the
_superuserscollection - Superusers can access and modify anything (collection API rules are ignored)
Authenticate with password
To authenticate with password you must enable the Identity/Password auth collection option (see also Web API reference ) .
The default identity field is the email but you can configure any other unique field like
"username" (it must have a UNIQUE index).
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
const authData = await pb.collection("users").authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
console.log(pb.authStore.isValid);
console.log(pb.authStore.token);
console.log(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout" the last authenticated record
pb.authStore.clear(); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
final authData = await pb.collection("users").authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
print(pb.authStore.isValid);
print(pb.authStore.token);
print(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout" the last authenticated record
pb.authStore.clear(); Authenticate with OTP
To authenticate with email code you must enable the One-time password (OTP) auth collection option (see also Web API reference ) .
The usual flow is the user typing manually the received password from their email but you can also
adjust the default email template from the collection options and add a url containing the OTP and its
id as query parameters
(you have access to {OTP} and {OTP_ID} placeholders)
.
Note that when requesting an OTP we return an otpId even if a user with the provided email
doesn't exist as a very rudimentary enumeration protection (it doesn't create or send anything).
On successful OTP validation, by default the related user email will be automatically marked as "verified".
Keep in mind that OTP as a standalone authentication method could be less secure compared to the other methods because the generated password is usually 0-9 digits and there is a risk of it being guessed or enumerated (especially when a longer duration time is configured).
For security critical applications OTP is recommended to be used in combination with the other auth methods and the Multi-factor authentication option.
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// send OTP email to the provided auth record
const result = await pb.collection('users').requestOTP('test@example.com');
// ... show a screen/popup to enter the password from the email ...
// authenticate with the requested OTP id and the email password
const authData = await pb.collection('users').authWithOTP(result.otpId, "YOUR_OTP");
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
console.log(pb.authStore.isValid);
console.log(pb.authStore.token);
console.log(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout"
pb.authStore.clear(); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// send OTP email to the provided auth record
final result = await pb.collection('users').requestOTP('test@example.com');
// ... show a screen/popup to enter the password from the email ...
// authenticate with the requested OTP id and the email password
final authData = await pb.collection('users').authWithOTP(result.otpId, "YOUR_OTP");
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
print(pb.authStore.isValid);
print(pb.authStore.token);
print(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout"
pb.authStore.clear(); Authenticate with OAuth2
You can also authenticate your users with an OAuth2 provider (Google, GitHub, Microsoft, etc.). See the section below for example integrations.
Before starting, you'll need to create an OAuth2 app in the provider's dashboard in order to get a Client Id and Client Secret, and register a redirect URL .
Once you have obtained the Client Id and Client Secret, you can enable and configure the provider from your PocketBase auth collection options (PocketBase > Collections > {YOUR_COLLECTION} > Edit collection (settings cogwheel) > Options > OAuth2).
This method handles everything within a single call without having to define custom redirects, deeplinks or even page reload.
When creating your OAuth2 app, for a callback/redirect URL you have to use the
https://yourdomain.com/api/oauth2-redirect
(or when testing locally - http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/oauth2-redirect ).
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('https://pocketbase.io');
...
// This method initializes a one-off realtime subscription and will
// open a popup window with the OAuth2 vendor page to authenticate.
//
// Once the external OAuth2 sign-in/sign-up flow is completed, the popup
// window will be automatically closed and the OAuth2 data sent back
// to the user through the previously established realtime connection.
//
// If the popup is being blocked on Safari, make sure that your click handler is not using async/await.
pb.collection('users').authWithOAuth2({
provider: 'google'
}).then((authData) => {
console.log(authData)
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
console.log(pb.authStore.isValid);
console.log(pb.authStore.token);
console.log(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout" the last authenticated record
pb.authStore.clear();
}); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
import 'package:url_launcher/url_launcher.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('https://pocketbase.io');
...
// This method initializes a one-off realtime subscription and will
// call the provided urlCallback with the OAuth2 vendor url to authenticate.
//
// Once the external OAuth2 sign-in/sign-up flow is completed, the browser
// window will be automatically closed and the OAuth2 data sent back
// to the user through the previously established realtime connection.
//
// Note that it requires the app and realtime connection to remain active in the background!
// For Android 15+ check the note in https://github.com/pocketbase/dart-sdk#oauth2-and-android-15.
final authData = await pb.collection('users').authWithOAuth2('google', (url) async {
// or use flutter_custom_tabs to make the transitions between native and web content more seamless
await launchUrl(url);
});
// after the above you can also access the auth data from the authStore
print(pb.authStore.isValid);
print(pb.authStore.token);
print(pb.authStore.record.id);
// "logout" the last authenticated record
pb.authStore.clear(); When authenticating manually with OAuth2 code you'll need 2 endpoints:
- somewhere to show the "Login with ..." links
- somewhere to handle the provider's redirect in order to exchange the auth code for token
Here is a simple web example:
Links page (e.g. https://127.0.0.1:8090 serving
pb_public/index.html):<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" /> <title>OAuth2 links page</title> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.7.1.slim.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="list"> <li>Loading OAuth2 providers...</li> </ul> <script type="module"> import PocketBase from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/pocketbase/js-sdk@master/dist/pocketbase.es.mjs" const pb = new PocketBase("http://127.0.0.1:8090"); const redirectURL = "http://127.0.0.1:8090/redirect.html"; const authMethods = await pb.collection("users").listAuthMethods(); const providers = authMethods.oauth2?.providers || []; const listItems = []; for (const provider of providers) { const $li = $(`<li><a>Login with ${provider.name}</a></li>`); $li.find("a") .attr("href", provider.authURL + redirectURL) .data("provider", provider) .click(function () { // store provider's data on click for verification in the redirect page localStorage.setItem("provider", JSON.stringify($(this).data("provider"))); }); listItems.push($li); } $("#list").html(listItems.length ? listItems : "<li>No OAuth2 providers.</li>"); </script> </body> </html>Redirect handler page (e.g. https://127.0.0.1:8090/redirect.html serving
pb_public/redirect.html):<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>OAuth2 redirect page</title> </head> <body> <pre id="content">Authenticating...</pre> <script type="module"> import PocketBase from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/pocketbase/js-sdk@master/dist/pocketbase.es.mjs" const pb = new PocketBase("http://127.0.0.1:8090"); const redirectURL = "http://127.0.0.1:8090/redirect.html"; const contentEl = document.getElementById("content"); // parse the query parameters from the redirected url const params = (new URL(window.location)).searchParams; // load the previously stored provider's data const provider = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("provider")) // compare the redirect's state param and the stored provider's one if (provider.state !== params.get("state")) { contentEl.innerText = "State parameters don't match."; } else { // authenticate pb.collection("users").authWithOAuth2Code( provider.name, params.get("code"), provider.codeVerifier, redirectURL, // pass any optional user create data { emailVisibility: false, } ).then((authData) => { contentEl.innerText = JSON.stringify(authData, null, 2); }).catch((err) => { contentEl.innerText = "Failed to exchange code.\n" + err; }); } </script> </body> </html>
When using the "Manual code exchange" flow for sign-in with Apple your redirect
handler must accept POST requests in order to receive the name and the
email of the Apple user. If you just need the Apple user id, you can keep the redirect
handler GET but you'll need to replace in the Apple authorization url
response_mode=form_post with response_mode=query.
Multi-factor authentication
PocketBase v0.23+ introduced optional Multi-factor authentication (MFA).
If enabled, it requires the user to authenticate with any 2 different auth methods from above (the
order doesn't matter).
The expected flow is:
- User authenticates with "Auth method A".
- On success, a 401 response is sent with
{"mfaId": "..."}as JSON body (the MFA "session" is stored in the_mfassystem collection). - User authenticates with "Auth method B" as usual
but adds the
mfaIdfrom the previous step as body or query parameter. - On success, a regular auth response is returned, aka. token + auth record data.
Below is an example for email/password + OTP authentication:
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
try {
await pb.collection('users').authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
} catch (err) {
const mfaId = err.response?.mfaId;
if (!mfaId) {
throw err; // not mfa -> rethrow
}
// the user needs to authenticate again with another auth method, for example OTP
const result = await pb.collection('users').requestOTP('test@example.com');
// ... show a modal for users to check their email and to enter the received code ...
await pb.collection('users').authWithOTP(result.otpId, 'EMAIL_CODE', { 'mfaId': mfaId });
} import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
try {
await pb.collection('users').authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
} on ClientException catch (e) {
final mfaId = e.response['mfaId'];
if (mfaId == null) {
throw e; // not mfa -> rethrow
}
// the user needs to authenticate again with another auth method, for example OTP
final result = await pb.collection('users').requestOTP('test@example.com');
// ... show a modal for users to check their email and to enter the received code ...
await pb.collection('users').authWithOTP(result.otpId, 'EMAIL_CODE', query: { 'mfaId': mfaId });
} Users impersonation
Superusers have the option to generate tokens and authenticate as anyone else via the Impersonate endpoint .
The generated impersonate auth tokens can have custom duration but are not renewable!
For convenience the official SDKs creates and returns a standalone client that keeps the token state in memory, aka. only for the duration of the impersonate client instance.
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// authenticate as superuser
await pb.collection("_superusers").authWithPassword("test@example.com", "1234567890");
// impersonate
// (the custom token duration is in seconds and it is optional)
const impersonateClient = await pb.collection("users").impersonate("USER_RECORD_ID", 3600)
// log the impersonate token and user data
console.log(impersonateClient.authStore.token);
console.log(impersonateClient.authStore.record);
// send requests as the impersonated user
const items = await impersonateClient.collection("example").getFullList(); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// authenticate as superuser
await pb.collection("_superusers").authWithPassword("test@example.com", "1234567890");
// impersonate
// (the custom token duration is in seconds and it is optional)
final impersonateClient = await pb.collection("users").impersonate("USER_RECORD_ID", 3600)
// log the impersonate token and user data
print(impersonateClient.authStore.token);
print(impersonateClient.authStore.record);
// send requests as the impersonated user
final items = await impersonateClient.collection("example").getFullList(); API keys
While PocketBase doesn't have "API keys" in the traditional sense, as a side effect of the support for
users impersonation, for such cases you can use instead the generated nonrenewable
_superusers impersonate auth token.
You can generate such token via the above impersonate API or from the
Dashboard > Collections > _superusers > {select superuser} > "Impersonate" dropdown option:
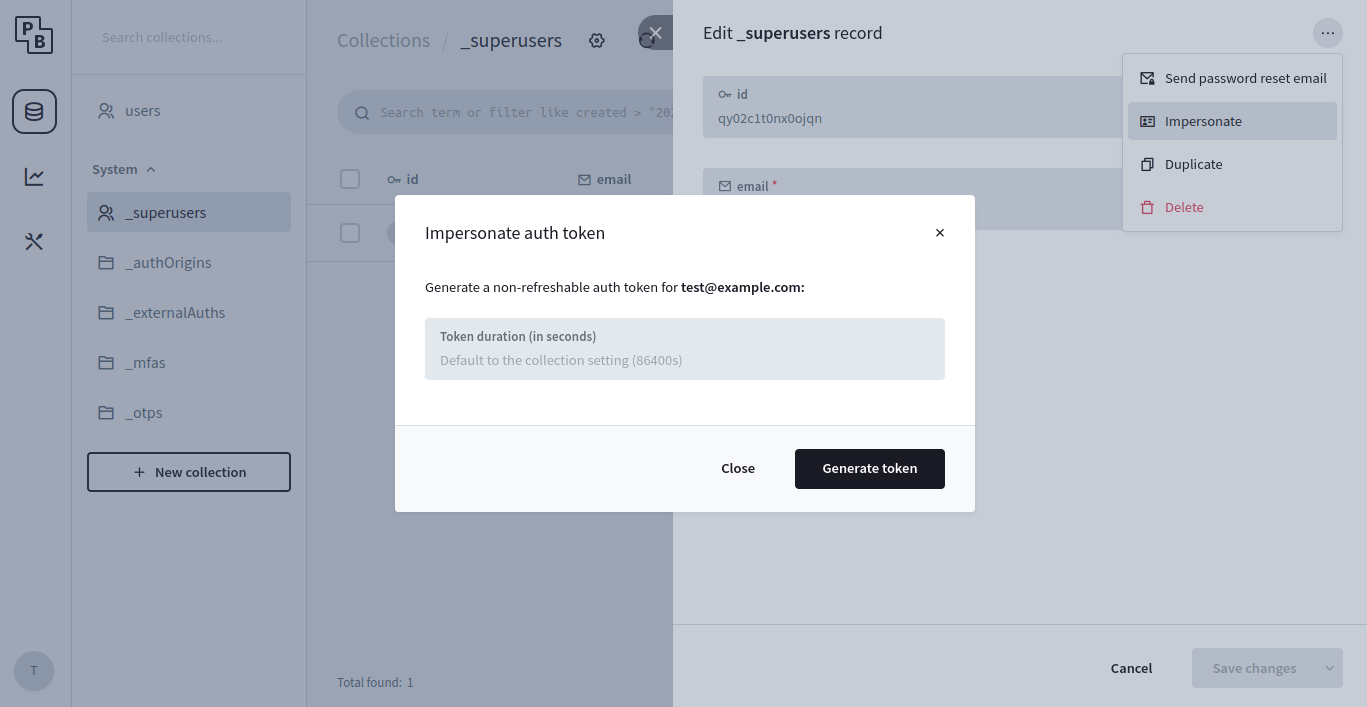
Because of the security implications (superusers can execute, access and modify anything), use the
generated _superusers tokens with extreme care and only for internal
server-to-server communication.
To invalidate already issued tokens, you need to change the individual superuser account password
(or if you want to reset the tokens for all superusers - change the shared auth token secret from
the _superusers collection options).
Auth token verification
PocketBase doesn't have a dedicated token verification endpoint, but if you want to verify an existing
auth token from a 3rd party app you can send an
Auth refresh
call, aka. pb.collection("users").authRefresh().
On valid token - it returns a new token with refreshed exp claim and the latest user data.
Otherwise - returns an error response.
Note that calling authRefresh doesn't invalidate previously issued tokens and you can safely disregard
the new one if you don't need it (as mentioned in the beginning - PocketBase doesn't store the tokens on the
server).
Performance wise, the used HS256 algorithm for generating the JWT has very little to no
impact and it is essentially the same in terms of response time as calling
getOne("USER_ID") (see
benchmarks
)
.