Uploading files
To upload files, you must first add a file field to your collection:
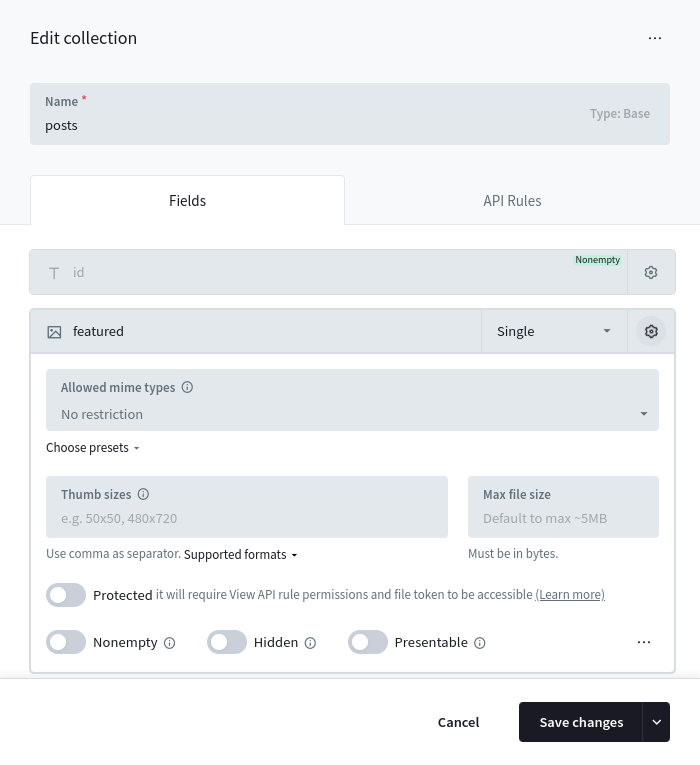
Once added, you could create/update a Record and upload "documents" files by sending a
multipart/form-data request using the Records create/update APIs.
Each uploaded file will be stored with the original filename (sanitized) and suffixed with a
random part (usually 10 characters). For example test_52iwbgds7l.png.
All file fields by default has a max allowed file size up to ~5MB (you can adjust it from the collection field options but keep in mind that allowing to upload
and serve large files could degrade the performance of your application).
Here is an example how to create a new record and upload multiple files to the example "documents"
file field using the SDKs:
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// create a new record and upload multiple files
// (files must be Blob or File instances)
const createdRecord = await pb.collection('example').create({
title: 'Hello world!', // regular text field
'documents': [
new File(['content 1...'], 'file1.txt'),
new File(['content 2...'], 'file2.txt'),
]
});
// -----------------------------------------------------------
// Alternative FormData + plain HTML file input example
// <input type="file" id="fileInput" />
// -----------------------------------------------------------
const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
const formData = new FormData();
// set regular text field
formData.append('title', 'Hello world!');
// listen to file input changes and add the selected files to the form data
fileInput.addEventListener('change', function () {
for (let file of fileInput.files) {
formData.append('documents', file);
}
});
...
// upload and create new record
const createdRecord = await pb.collection('example').create(formData); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// create a new record and upload multiple files
final record = await pb.collection('example').create(
body: {
'title': 'Hello world!', // regular text field
},
files: [
http.MultipartFile.fromString(
'documents',
'example content 1...',
filename: 'file1.txt',
),
http.MultipartFile.fromString(
'documents',
'example content 2...',
filename: 'file2.txt',
),
],
); If your file field supports uploading multiple files (aka.
Max Files option is >= 2) you can use the + prefix/suffix field name modifier
to respectively prepend/append new files alongside the already uploaded ones. For example:
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
const createdRecord = await pb.collection('example').update('RECORD_ID', {
"documents+": new File(["content 3..."], "file3.txt")
}); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
final record = await pb.collection('example').update(
'RECORD_ID',
files: [
http.MultipartFile.fromString(
'documents+',
'example content 3...',
filename: 'file3.txt',
),
],
); Deleting files
To delete uploaded file(s), you could either edit the Record from the Dashboard, or use the API and set
the file field to a zero-value
(empty string, []).
If you want to delete individual file(s) from a multiple file upload field, you could
suffix the field name with - and specify the filename(s) you want to delete. Here are some examples
using the SDKs:
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// delete all "documents" files
await pb.collection('example').update('RECORD_ID', {
'documents': [],
});
// delete individual files
await pb.collection('example').update('RECORD_ID', {
'documents-': ["file1.pdf", "file2.txt"],
}); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// delete all "documents" files
await pb.collection('example').update('RECORD_ID', body: {
'documents': [],
});
// delete individual files
await pb.collection('example').update('RECORD_ID', body: {
'documents-': ["file1.pdf", "file2.txt"],
}); The above examples use the JSON object data format, but you could also use FormData instance
for multipart/form-data requests. If using
FormData set the file field to an empty string.
File URL
Each uploaded file could be accessed by requesting its file url:
http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/files/COLLECTION_ID_OR_NAME/RECORD_ID/FILENAME
If your file field has the Thumb sizes option, you can get a thumb of the image file by
adding the thumb
query parameter to the url like this:
http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/files/COLLECTION_ID_OR_NAME/RECORD_ID/FILENAME?thumb=100x300
Currently limited to jpg, png, gif (its first frame) and partially webp (stored as png).
The following thumb formats are currently supported:
- WxH (e.g. 100x300) - crop to WxH viewbox (from center)
- WxHt (e.g. 100x300t) - crop to WxH viewbox (from top)
- WxHb (e.g. 100x300b) - crop to WxH viewbox (from bottom)
- WxHf (e.g. 100x300f) - fit inside a WxH viewbox (without cropping)
- 0xH (e.g. 0x300) - resize to H height preserving the aspect ratio
- Wx0 (e.g. 100x0) - resize to W width preserving the aspect ratio
The original file would be returned, if the requested thumb size is not found or the file is not an image!
If you already have a Record model instance, the SDKs provide a convenient method to generate a file url by its name.
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
const record = await pb.collection('example').getOne('RECORD_ID');
// get only the first filename from "documents"
//
// note:
// "documents" is an array of filenames because
// the "documents" field was created with "Max Files" option > 1;
// if "Max Files" was 1, then the result property would be just a string
const firstFilename = record.documents[0];
// returns something like:
// http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/files/example/kfzjt5oy8r34hvn/test_52iWbGinWd.png?thumb=100x250
const url = pb.files.getURL(record, firstFilename, {'thumb': '100x250'}); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
final record = await pb.collection('example').getOne('RECORD_ID');
// get only the first filename from "documents"
//
// note:
// "documents" is an array of filenames because
// the "documents" field was created with "Max Files" option > 1;
// if "Max Files" was 1, then the result property would be just a string
final firstFilename = record.getListValue<String>('documents')[0];
// returns something like:
// http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/files/example/kfzjt5oy8r34hvn/test_52iWbGinWd.png?thumb=100x250
final url = pb.files.getURL(record, firstFilename, thumb: '100x250'); Additionally, to instruct the browser to always download the file instead of showing a preview when
accessed directly, you can append the ?download=1 query parameter to the file url.
Protected files
By default all files are publicly accessible if you know their full url.
For most applications this is fine and reasonably safe because all files have a random part appended to their name, but in some cases you may want an extra security to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive files like ID card or Passport copies, contracts, etc.
To do this you can mark the file field as Protected from its field options in the
Dashboard and then request the file with a special short-lived file token.
Only requests that satisfy the View API rule of the record collection will be able to access or download the protected file(s).
import PocketBase from 'pocketbase';
const pb = new PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// authenticate
await pb.collection('users').authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
// generate a file token
const fileToken = await pb.files.getToken();
// retrieve an example protected file url (will be valid ~2min)
const record = await pb.collection('example').getOne('RECORD_ID');
const url = pb.files.getURL(record, record.myPrivateFile, {'token': fileToken}); import 'package:pocketbase/pocketbase.dart';
final pb = PocketBase('http://127.0.0.1:8090');
...
// authenticate
await pb.collection('users').authWithPassword('test@example.com', '1234567890');
// generate a file token
final fileToken = await pb.files.getToken();
// retrieve an example protected file url (will be valid ~2min)
final record = await pb.collection('example').getOne('RECORD_ID');
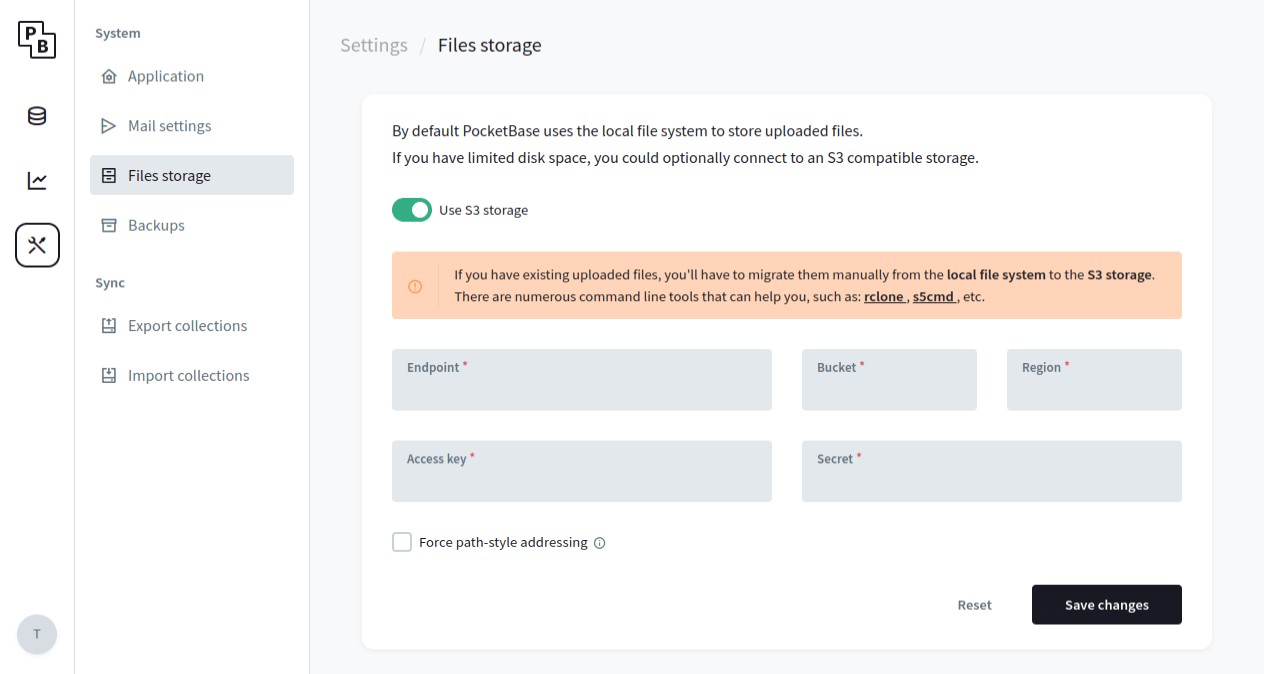
final url = pb.files.getURL(record, record.getStringValue('myPrivateFile'), token: fileToken); Storage options
By default PocketBase stores uploaded files in the pb_data/storage directory on the local file
system. For the majority of cases this is usually the recommended storage option because it is very fast, easy
to work with and backup.
But if you have limited disk space you could switch to an external S3 compatible storage (AWS S3, MinIO, Wasabi, DigitalOcean Spaces, Vultr Object Storage, etc.). The easiest way to set up the connection settings is from the Dashboard > Settings > Files storage: